RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a technology that utilizes radio waves to identify individuals or objects. With this technology, data is exchanged between a device called a’reader’ and an electronic tag. A tag is attached to an object. This technology is commonly used to know the location of people or objects. According to “Harrods’s Librarian’s Glossary and Reference Book,” RFID is an alternative to barcodes that uses tiny microchips embedded in tags to store and exchange data about an object.
Components of RFID System:
A) RFID Tag:
An RF ID tag is a tiny radio device, also known as a transponder, smart tag, smart level, or radio barcode. RFID tags have two parts. The first is a small silicon chip or integrated circuit that contains some other identification mark (ID) or information. Second, an antenna, which receives or transmits radio waves. Inside the antenna is a metal heat/conductive coil.
B) Reader and Antenna:
The main function of the reader is to query the tag and receive data from it. The RFID reader converts the radio waves from the RFID tag into a form that can be sent to intermediary software. The antenna of the RFID reader can communicate with the RFID chip. It can read the information stored in the tag and ‘update’ it with new information. By doing this, the RFID reader does two things: it receives commands from the control software and sends them to the tag.
C) Middleware (intermediary software):
The middleware receives the data from the RFID tag, sends it to the appropriate destination and performs some filtering and control functions. RFID middleware retrieves data from the reader, sends filtering data to application software, reports object movement information, and provides information about tag and reader network performance.
D) Server:
A server is a communication medium between different parts of an RFID enabled system. It receives information from one or more readers and matches it with information stored in a server database or exchanges information with library software. The server usually has a transaction database, which can be used to generate various reports related to transactions.

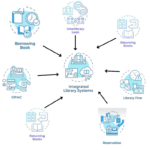
RFID Components of Libraries:
1. RFID tag
It is paper thin, flexible and approximately 2″ X 2″ in size. As a result, it can easily be placed anywhere inside the book. Attached to it is an antenna or a tiny chip that contains the bibliographic data of the book and a unique identifier to identify each book.
2. Self-Check-out Station:
A station consists of a computer with a touchscreen and a belt-in RFID reader, software necessary to identify library members and library materials, and perform circulation functions. With self-check-out stations, library members can borrow books by following a touchscreen menu without the help of a library staff.
3. Book Drop (Return Station)
The system includes ‘book drop’ counters with special monitors and printers. It allows library members to return borrowed materials. As he ‘drops’ the book here, the reader embedded in it reads the RFID tag. The material is then automatically accepted into the library, dismissed from the name of the person concerned, and material security activities are resumed.
4. Security door
A security gate or ‘Electronic Art Surveillance’ is a method of preventing material theft. The main function of this gate is to prevent the removal of material from the library that has not been legitimately borrowed. One of the features of the chip embedded in the RFID tag is to prevent theft. For this purpose, the chip identifies the material. Acts both to commit and to prevent theft.
5. Automatic Sorting Station:
Automated sorting machines receive books from the “return station”, ‘check-in’ them to the librarian, and distribute them into multiple bins or containers for re-shelving. Automatically identifies the shelf position of books and arranges to place them there quickly. Some libraries use sorters with multiple book-drop readers. These sorters also have conveyor belts that bring the books from the book drop counter to the sorter.
6. Staff Workstation:
A staff wire station consists of a reader and a personal computer. With its help, lending and taking back materials, document sorting, etc. are done. Programming/tagging is done with it on new library content. For this, it is placed on the reader, its accession number is read with the help of a barcode scanner, and then the corresponding bibliographic data is downloaded from the automation software of the library.
7. Inventory Control:
This is done to check the stock of books or know the position of books on the shelf. A portable reader is used for this purpose. The reader sends the book ID to the library software through the server and quickly retrieves the book information in response. It greatly eases the work of the librarian for locating books/library material.
Implementation of RFID in libraries:
a) Each item of library integrated software includes full bibliographic information;
b) When the reader comes to borrow or return an item, the RFID reader reads the required information from the item tag and sends it to the software.
c) The collection is then issued quickly, without the assistance of library staff;
d) When the reader takes the material out of the library, the antenna installed at the exit gate automatically reads the data of the book’s RFID tag to know whether the book has been issued correctly. Provide alerts or warnings if it detects that the book is not validly issued;
e) RFID is being widely used not only in circulation but also in library stock checking or stock taking.
Advantages of using RFID in libraries:
1. Quick Content Transaction:
Due to the use of RFID, circulation work takes much less time. Data can be read from RFID tags much faster than barcodes or other commonly used methods, and multiple content data can be read simultaneously.
2. Facility of borrowing or returning books by the reader:
Through RFID technology, the reader/holder can issue and return books or library material himself. Any reader can do the job without the help of a librarian.
3. Speedy overall list preparation and honey verification:
They can be scanned with anything from themselves to book in the RFID system. The identification information can be read as soon as the self-book is touched to the portable RFID reader. Wireless technology not only allows for up-to-date information on inventory, but also lets you know if a book is out of place.
4. Longevity of Tag:
RFID tags last much longer than normal barcodes. Most RFID service providers guarantee 100,000 transactions per tag.
5. More security:
Greater security can be ensured thanks to RFID technology. It is possible to detect and prevent theft without much additional cost
6. Enhanced readership:
In addition to RSIDA, it helps improve staff productivity by saving time and labor of librarians, thereby improving reader service.
RFID technology in libraries has transformed asset management by allowing for efficient tracking and quick inventory of books. This innovation significantly reduces the time spent on manual tasks. Additionally, RFID enables libraries to better meet the needs of modern users, making resources more accessible and enhancing the overall library experience.