The importance of information as a key driver of economic and social development is widely acknowledged in the modern world. This recognition did not happen overnight; it can be traced back to the industrial revolution, which brought significant changes to social structure from the mid-18th to the mid-19th century. The working class shifted from agriculture to industry. In 1970, 80% of the world’s population was engaged in agriculture, dropping to 60% by 1950. Agriculture became the largest production after the world wars, but the emergence of the information society changed the situation again.
The information society is often referred to as the “Third Wave” in the development of human civilization. This represents a shift where information has become the key strategic raw material and asset.
An information society
An information society relies on information and communication technologies (ICTs) and the widespread use of information and knowledge as key drivers of economic, social, and cultural activities. Here are five key characteristics that help define an information society:
1. Access to Information: High access to information and knowledge through the internet, digital media, libraries, and educational institutions.
2. Digital Connectivity: Widespread digital connectivity enables instant communication, collaboration, and information sharing.
3. Knowledge Economy: Economies driven by the production, distribution, and utilization of knowledge and information.
4. Technological Innovation: Continuous technological innovation and advancement are shaping various aspects of society.
5. Information Literacy: Emphasis on the ability to access, evaluate, and effectively use information from various sources.
Information technology (IT)
These characteristics highlight the transformative impact of information and communication technologies on society, the economy, and culture, emphasizing the importance of access to information, digital connectivity, knowledge creation, technological innovation, and information literacy in shaping the dynamics of an information society.
Information technology (IT) encompasses a wide range of concepts, tools, and processes. Here are five key characteristics that help define IT:
1. Data Handling: IT involves the management, storage, retrieval, and processing of data. This includes databases, data analysis, data security, and ensuring the integrity and availability of data.
2. Communication: IT facilitates communication through various means, such as email, messaging apps, video conferencing, and collaborative platforms. It enables real-time communication and collaboration among individuals and organizations, regardless of geographical boundaries.
3. Automation: IT often involves automating tasks and processes to improve efficiency and productivity. This includes using software, scripts, and algorithms to streamline repetitive tasks, minimize errors, and optimize resource utilization.
4. Networking: Networking is a fundamental aspect of IT, involving the interconnection of devices and systems to facilitate data exchange and communication. This includes local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), the internet, and emerging technologies like cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT).
5. Security: IT encompasses various measures and protocols to protect data, systems, and networks from unauthorized access, cyber threats, and data breaches. This includes encryption, firewalls, antivirus software, access controls, and cybersecurity best practices.
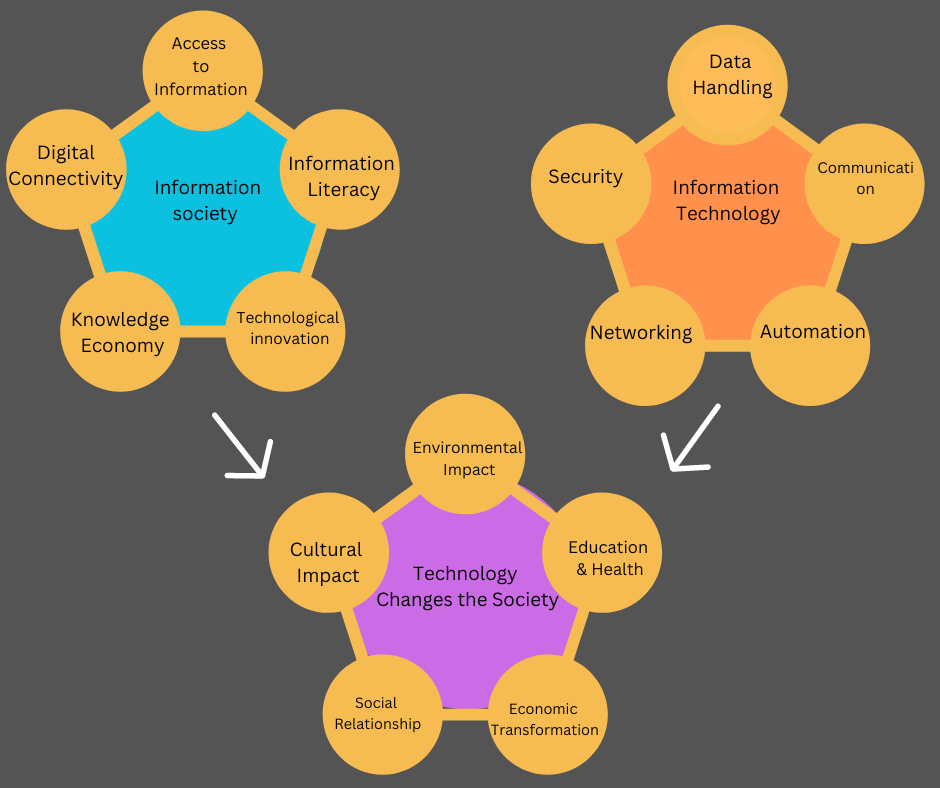
How technology changes society:
Technology has profound effects on society, influencing various aspects of human life. Here are several ways in which technology changes society:
Communication: Technology has revolutionized how people connect, share information, and builds relationships through social media, messaging apps, and video conferencing.
Access to Information: The internet has democratized access to knowledge, empowering individuals to educate themselves and participate more actively in society.
Economic Transformation: Technology has created new industries and business models while disrupting traditional ones through automation, e-commerce, and digital payments.
Social Relationships: Technology alters how people communicate and form connections, providing opportunities for virtual interactions but also leading to challenges such as decreased face-to-face communication.
Education: Technology has expanded educational opportunities and personalized learning experiences through online platforms and digital classrooms.
Healthcare: Advancements such as telemedicine and wearable devices have enhanced diagnosis, treatment, and patient care.
Cultural Impact: Technology shapes cultural expression and consumption patterns through social media, streaming platforms, and digital art.
Environmental Impact: While renewable energy contributes to sustainability efforts, the production and disposal of electronic devices can lead to environmental degradation and e-waste pollution.



