Data Communication: How the commonly used characters, symbols, numbers, etc. used in the language are converted into machine text language and become bits and bytes. To maintain the international standard of this bit or byte conversion, there are various encodings called ASCII to Unicode. The ASCII (7 bit) encoding contains 128 characters, while the ASCII (8 bit) or EBCDIC encoding contains 256 characters. Currently, more than 65,000 characters can be expressed using Unicode. Using this Unicode, it has been possible to make almost all the major and popular regional languages of the world understandable to computers by converting them into machine text. English language or ASCII is no longer as important as it was before as a data encoding and machine text language.
Just as any data in a computer is stored through the signal 0 or 1, the amount of signal that can be transmitted through various media is measured through Hertz or bandwidth. The unit of measurement for signal flow is called Hertz. It is measured in Hertz as the distance of one complete cycle of an electromagnetic wave per second.
Just as any data in a computer is stored through the signal 0 or 1, the amount of signal that can be transmitted through various media is measured through Hertz or bandwidth. The unit of measurement for signal flow is called Hertz. It is measured in Hertz as the distance of one complete cycle of an electromagnetic wave per second.
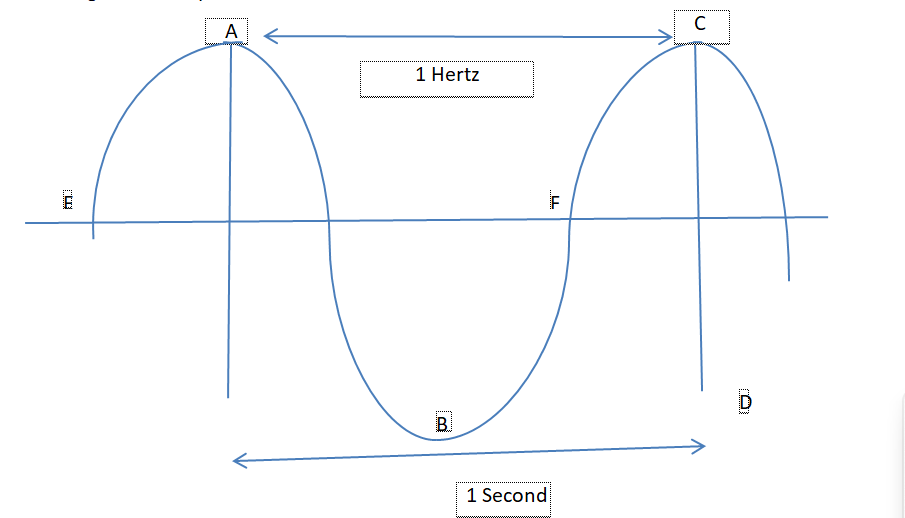
According to the above figure, in one second the wave completes one cycle between the distance A-B-C. Therefore, the distance A-C will be called one Hertz. Alternatively, the length E-F can also be called one Hertz.
The distance a wave travels in one second or the length it crosses to complete one cycle in one second is called one Hertz.
One kilo Hertz = 1000 Hertz. One mega Hertz = 1000000 Hertz.
The maximum and minimum cycles transmitted through a conductor in 1 second is called bandwidth. According to the above figure, the distance between C and D can be called 1 bandwidth. Usually, a high-power broadcasting medium such as television transmits 30-300 mega Hertz signals for data transmission. We usually call this type of bandwidth broadband.
The speed at which data is transmitted through a conductor is called the baud rate. Its unit is called Baud. 1 Baud = 1 bit per second. Nowadays, the baud rate between any two computers is 2400-4800 baud.
Digital and Analog Communication:
The type of data communication depends on the signal.
Signals can be of two types:
1. Analog signal: It is a type of continuous but changing electrical wave.
2. Digital signal: It is a discrete electrical current flowing in a sequential manner.
Analog signal is a commonly used communication medium. The signal used in telephone lines is an analog signal. On the other hand, digital signal is converted into two-dimensional form (0,1) with the help of a special device and sent through the transport medium. In the case of a computer, the data is directly converted and coupled through that special device is called a modem.
Naturally, digital signal flow takes more time but the quality of data is perfect and of high quality. Analog signal is very fast but the tendency is very high due to the low quality received at the other end. Digital signal is of two types –
1. Synchronous: Here the data is affected regularly and systematically.
2. Aynchoronous: Here each letter of the data is affected separately, one by one, at irregular intervals.
Communication methods:
Communication methods generally follow three types of methods.
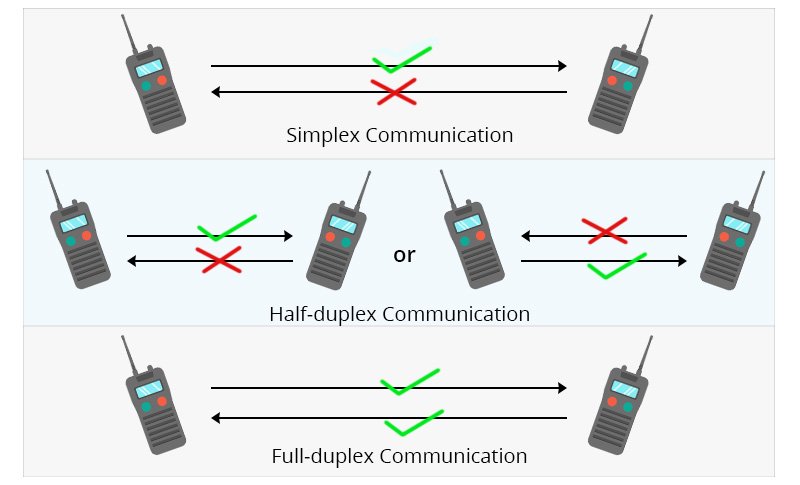
1. Simplex communication: In this method, criticism is one-way. The recipient can only listen but cannot respond. Currently, this method is almost obsolete.
2. Half-duplex method: In this two-way method, it can be from both sides of the society. But it can only flow in one direction at a time.
3. Full-duplex method: In this method, communication can flow in both directions at the same time. For example, in the case of telephone communication, the sender and the receiver can exchange information simultaneously without interruption. In today’s online or Internet era, data commun
ication occurs between two computers in a full duplex manner.
Connection medium:
Apart from telephone lines, there are many other connection mediums. For example, hard wire, coaxial cable, microwave, infrared, laser, artificial satellite etc. The simplest and most widely used medium among them is wire. Wire is used in various ways as a medium.
1. Twisted pair of wires:
Here two wires are twisted together and connected as a single wire between two devices. This type of wire is used to transmit very small signals.
a. Low cost;
b. Easily replaceable;
c. Very easy to control;
d. Low pollution;
e. Speed 4 megabits per second;
f. Can connect about 1000 devices at a time
e. The network can be extended up to half a mile in length
2. Coaxial cable:
Here two wires are laid together but one of them is covered by a very fine metal wire woven tube. The other wire is covered by a non-conductive cover and extends through the center of this tube.
The characteristics of this medium are:
a. Widely economical;
b. High bandwidth but prone to pollution;
c. Speed up to 10 megabits per second;
d. Control is more complicated than twisted pair;
e. More expensive than the previous one;
In the survey, two types of Ethernet cables are used, thick and thin. Thick Ethernet can send signals up to about 500 meters and thin Ethernet up to about 180 meters or 500 feet. Usually, Ethernet cables are connected with two-inch diameter BNC connectors.
Twisted pair cables are connected via RJ-45 connectors.
This allows signals to be sent from the workstation to the hub, which is located at a maximum distance of 100 meters.
3. Optical fiber cable:
A cable made of fine, light-emitting, brownish-purple plastic strands like hairs wrapped with a special type of non-conductive material is called an optical fiber cable.
Twisted pair or coaxial cable is capable of transporting electrical waves, but optical fiber is capable of transporting electrical waves. Lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are used to convert electrical waves into light waves.
Characteristics of optical fiber cable –
a. Due to its very high bandwidth capacity, the data transmission capacity is very high;
b. The level of radiation pollution is almost zero;
c. It is almost impossible to say that information is lost through radiation;
d. Light waves cannot be easily monitored;
e. The cable line can be extended as far as desired without repeaters.
In conclusion, data communication forms the backbone of modern digital interaction by converting human-readable language into machine-readable binary code through encoding systems like ASCII and Unicode. With the advancement of high-speed transmission media such as optical fiber, communication today has become faster, more reliable, and globally interconnected.