Catalog Entry: Library index A document or list of the collection of a library that meets users’ information needs. According to the needs of users, different unit records have to be created for textual material. We call these collections. Every dialogue is made for the user’s use. So writing is created by paying attention to the user’s request. So writing, composition, or entry means to meet the requirements of life users; a library catalog is prepared to consist of various unit records, called entries. Each entry is designed to satisfy a particular user approach.
Library catalogs are organized into a number of unit records to meet the needs of users. Each collection or entry is created to meet the needs of the reader. For each book, one main and multiple supporting entries are created. Generally, users search for text materials through three types of applications.
1. Author
2. Subject
3. Title.
Also, in some cases, they search by series.
Dictionary catalogs are described in AACR 1 (P-344) and AACR 2. “The dictionary catalog is a catalog in which all entries (authors, titles, series, etc.) and their related references are arranged together in one general alphabet; sub-arrangement frequently varies.”
In light of the above description, the entries or entries in the library index can be divided as follows:
1. Main entry
2. Additional entry
3. Reference or Cross Reference Entries
Also, the list is considered a unit card.
- Main Entry: A main record or entry has to be prepared for each text collected in the library. AACR 1 (P-344) and AACR 2 (P-567) have been mentioned as the main record or entry—”The main entry is the complete catalog record of a bibliographical entity, presented in the form by which the entity is to be uniformly identified and cited. The main entry normally includes the tracing of all other headings under which the record is to be represented in the catalog.”
The writing prepared with all the essential information of a work is called the main text or writing. The main text or writing is usually prepared by a personal or anonymous author. However, if there are more than three authors or editors, the main text has to be prepared under the title. Moreover, some reference books, including religious texts, encyclopedias, and dictionaries, have to be prepared under the title. The main text contains tracing. The tracing contains references to additional writings of specific text content. The headings of the main text are as follows:
a. Personal name of the author
b. Name of the institution or organization
c. Name or title of the book
If there is one author, then the heading is under the personal name of the author; if there are two or three, then under the name of the main author; and if there are more than three authors, then under the title. If the book is a collection of works by different authors, then under the name of the collection, and if it is a corporate body, then under the title.
2. Added Entry: After the main entry is prepared, the entries or entries that are ready as additional or auxiliary entries are called secondary entries.
AACR 2 (P-563) states that “An added entry and an entry additional to the main entry, by which an item is represented in a catalog, is a secondary entry.”
Additional writing acts as a supplement to the main writing or collection. The additional writings that are created for a text are –
a) Subject
b) Joint Author
c) Editor
d) Translator
e) Illustrator
f) Title
g) Series
h) First or main author about more than three authors
3. Reference Entries: In some cases, reference entities have to be prepared for special instructions. That is, the signals by which instructions are given from one subject to another are called reference entities.
AACR 2 (page 569) states that reference is a direction from one heading or entry to another.”
In this regard, we see three things:
- See Reference
- See also Reference
- Cross Reference
a. See Reference: See References are used to refer from a heading not used in the catalog to the heading used in the catalog. In the case of the Learning and Scholarship subject title, the writing should be done in the following format:


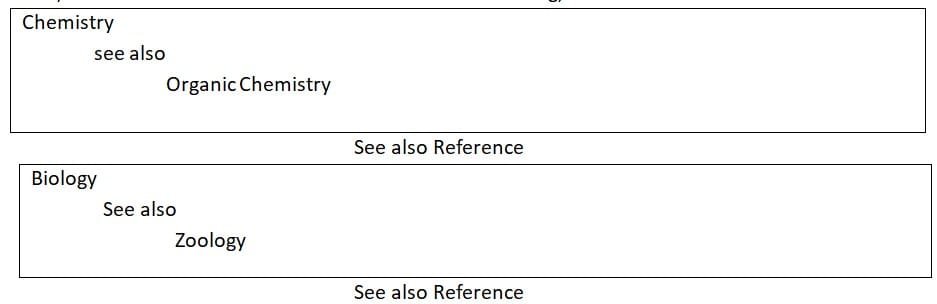
b. See also Reference: “See also” is used for related topics. In this case, if one heading is used in the index, a “see also” card is created for another related heading, such as:
c. Cross Reference: Cross references are used between See Reference and related headings, except for See also. Cross references are given in two ways. For example:

AACR 1 and AACR 2 recognize the See Reference and See Also references as reference links. However, many information specialists do not recognize reference cards as catalog entries. They argue that such links do not contain any information about the text. They merely direct or refer the reader from one heading to another.
The catalog entry of a library collection is one of the most important documents in the process of communication. The mirror of the library collection is the catalog. The catalog entry indicates the identification and location of books and other reading materials. Users come to the library to fulfill their library needs. In this case, the catalog entry plays a leading role in getting the information they need quickly without wasting users’ time. In the overall sense, the catalog entry is observed to have many functions.
The importance and functions of the catalog entry are discussed below:
- Arrange the titles of books and other reading materials in the library in such a way that the reader has the least chance of finding the author, title, subject, editor, translator, illustrator, compiler, series, or any person or organization related to the book.
- A library can find out what publications by a particular author are available in the library through an author entry.
- A library can find out what publications by a particular author are available in the library through an author entry.
- The writing in the catalog is prepared in such a way that the reader can easily find the specific text material and meet the reading needs by knowing only the author, title, series, or subject.
- With the help of cross-reference, the reader gets directions to go from one title to another or see more.
- The strength or weakness of the collection on a particular subject in the library is known through the catalog entry. In this, the librarian can arrange to select and collect the necessary books.
- The catalog entry is used as a reference for reading materials and as an effective tool for collecting information.
- It is known what proposals are available in the library under a series.
- The catalog entry is known through the catalog entry what books are available in a particular library from a publisher.
- Through the catalog entry, it is known whether there is a series of a particular book collected.
Just as the catalog entry helps in organizing the reading materials neatly and beautifully, it also plays an effective role in retrieving information according to the needs of the user. In this era of information technology, the catalog entry helps in controlling the bibliography. Above all, it can be said that the catalog entry is a necessary and important element of the library.



