Information literacy is a critical competency that involves understanding the nature of information and its effective utilization. It empowers individuals to seek truth rather than merely collecting facts. By teaching the skills to locate, evaluate, and use information judiciously, information literacy serves as an essential tool for critical thinking, especially in an era rife with misinformation. Being information literate signifies that one is a knowledgeable and ethical user of information.
An example of information literacy can be seen when a student is assigned to write a research paper on climate change and follows these steps:
1. Identifies the need for information – The student recognizes that to write the paper, they need credible scientific data and expert opinions.
2. Searches effectively – They utilize library databases, Google Scholar, and reputable environmental websites to find reliable sources.
3. Evaluates sources – The student checks the authorship of the information, determines whether it comes from a peer-reviewed journal or a biased blog, and assesses the recency of the data.
4. Uses information ethically – They take notes, summarize findings, and cite sources properly to avoid plagiarism.
5. Applies knowledge – The student combines information from multiple sources to create a clear and well-supported argument in the paper.
According to the American Library Association (1989), “Information literacy is a set of abilities requiring individuals to recognize when information is needed and have the ability to locate, evaluate, and use effectively the needed information.”
Information Literacy is vital across various domains:
1. Academic Success: For students, faculty, and researchers, information literacy is essential for effective learning and research, enabling them to access reliable sources and construct well-informed arguments.
2. Workplace Success: In professional settings, information literacy contributes to successful business operations and employment prospects, as employees who can adeptly find and use information are more valuable to their organizations.
3. Knowledgeable Citizens: Information literacy is also a right for citizens, fostering informed decision-making and active participation in civic life. It empowers individuals to engage with societal issues thoughtfully and responsibly.
Information literacy is foundational for academic achievement, workplace effectiveness, and informed citizenship, making it a crucial aspect of education and lifelong learning.
Importance of Information literacy
Information literacy is essential because it empowers individuals to find, evaluate, use, and share information effectively and responsibly. In today’s information-rich world, being information literate is as crucial as being able to read and write. Here are the main reasons why information literacy is so important:
1. Critical Thinking and Decision-Making:
Information literacy teaches individuals to question sources, analyze evidence, and make informed decisions instead of accepting information at face value.
2. Academic and Research Success:
Students and researchers depend on credible information. Information literacy enables them to locate reliable data, cite sources correctly, and avoid plagiarism.
3. Workplace Competence:
In professional environments, employees must process large amounts of data and information. Information literacy allows them to solve problems efficiently and make data-driven decisions.
4. Digital and Media Awareness:
In the age of social media and misinformation, information literacy helps individuals recognize falsehoods, biases, and propaganda.
5. Lifelong Learning:
Information literacy is not confined to school or work; it is a lifelong skill that supports personal growth, continuous learning, and adaptability in a changing world.
6. Empowered Citizenship:
Informed citizens contribute more effectively to society and democracy by understanding issues, policies, and credible sources of information.
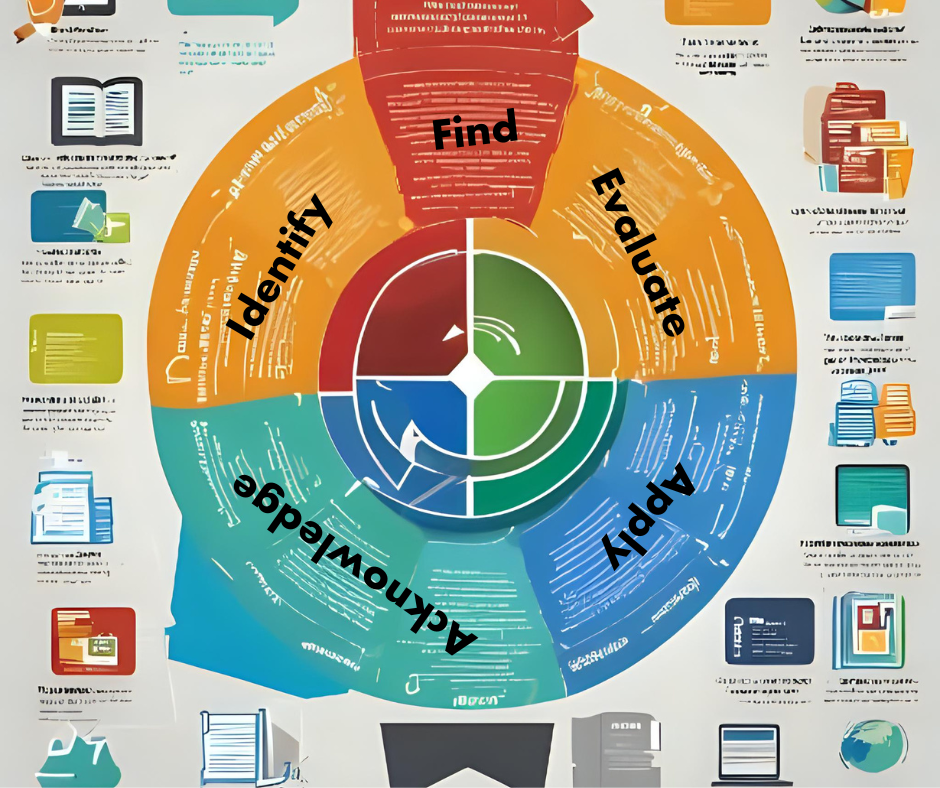
The Five Essential Components of Information Literacy:
Information literacy encompasses five crucial components that are integral to effectively navigating and utilizing information in various contexts.
1. Identify
The first step in information literacy is recognizing the necessity of acquiring relevant information. This involves taking the time to articulate and define the specific problem or query at hand, ensuring that all key aspects and underlying factors are completely understood.
Interpretation
– Acknowledge when the need for information arises.
– Clearly define the scope and purpose of the information you seek.
– Formulate precise research questions or articulate the information problem to direct your search effectively.
2. Find
Once the information needs are identified, it is essential to employ well-defined strategies and make use of advanced tools tailored to your specific requirements. This stage is crucial for gathering thorough and precise information about the subject.
Interpretation
– Utilize appropriate tools and techniques designed to locate pertinent information efficiently.
– Skillfully navigate through various information sources, including search engines, library catalogs, academic databases, and other relevant resources to ensure comprehensive research.
3. Evaluate
In this component, you must critically assess the reliability, relevance, and accuracy of the information collected. This assessment involves scrutinizing the source of the information, its credibility, and the context in which it was created. It’s also vital to determine the timeliness of the information and its consistency with established facts and data from authoritative references.
Interpretation
– Exercise judgment regarding the reliability and credibility of information sources, including evaluating potential bias.
– Differentiate between objective facts, subjective opinions, and persuasive propaganda to ensure informed decision-making.
4. Apply
The next step is to systematically apply, organize, and utilize the collected information in a manner that is both ethical and purposeful. This means integrating the various pieces of information to create new knowledge or solve specific problems.
Interpretation
– Effectively organize the information gathered to facilitate understanding.
– Utilize the information in a legal and ethical manner, diligently citing all sources to uphold academic integrity.
5. Acknowledge
The final component involves sharing the knowledge gained with others in a clear, engaging, and understandable manner. This entails selecting appropriate formats for communication that enhance the retention and comprehension of the information being shared.
Interpretation
– Present findings or information using suitable formats—whether written, oral, or digital—to engage the intended audience effectively.
– Adapt communication strategies and tools based on the needs and preferences of the audience to optimize understanding.
Information literacy is a vital competency for students, educators, researchers, information professionals, and librarians. It is imperative for all stakeholders within the information realm to be well-versed in the five components of information literacy: Identify, Find, Evaluate, Apply, and Acknowledge. Mastery of these components is essential for navigating the complex landscape of information and making informed decisions.