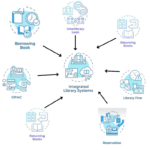
Modern Library Computer based cataloging is popular in the country. A computer is an automatic device that can store entries, add new entries or withdraw them. Computer entries are automatically generated in machine readable form. They are stored by input. Later, when needed, they are retrieved through output. This is called online cataloging. The system is directly linked to the computer. It can be used at any time for immediate need.
Computer-Based Cataloging Systems and Online Cataloging
Online catalogue, through search systems as the Dynix software development in 1983 and used widely through the late 1990s, has greatly enhanced the usability of catalogues thanks to the rise of MARC standards (an acronym for machine-readable catalogue in the 1960s.
Evolution of Online Public Access Catalogs (OPACs)
Rules governing the creation of MARC catalogue records include not only formal cataloging rules such as Anglo-American cataloging rules, second edition (AACR2). Resource Description and Access(RDA), but also rules specific to MARC, available from the U.S. Library of Congress and the OCLC, the online computer library Center, a global Cooperative that builds and maintains WorldCat.
Role of MARC Standards in Automated Cataloging
MARC was originally used to automate the creation of physical catalogue cards, but its use evolved into direct access to the MARC computer files during the search process.
OPACs have enhanced usability over traditional card format because:
1. The online catalogue does not need to be stored statically; the user can choose author, title, keyword, or systematic order dynamically.
2. Most online catalogue allow searching for any word in a title or other field , increasing the ways to find a record.
3. Many online catalogues allow links between several variants of an author’s name.
4. The elimination of paper cards has made the information more accessible to many people with disabilities, such as the visually impaired, wheelchair users, and those who suffer from mould allergies or other paper or building-related problems.
5. Physical storage space is considerably reduced.
6. Updated are significantly more efficient.
Features, Functions and Requirements of Automatic Cataloging: When the system of a library or information center is operated through the use of computers and other information technology, it is called an online system. That is, when a library uses computers and other technologies to index the library or information center, it is called an automated cataloging system.
Objectives of Implementing Automated Library Systems
Apart from the manual cataloging system, there are many reasons for implementing the current modern system which is an automated/online system. Automated library systems have been introduced in almost every information center or library, replacing the old methods. The objectives and utilities of automated cataloging are discussed below.
1. Vast Processing Capacity:
Computers can process vast amounts of material, information and data which are impossible to do manually.
2. Greater Speed and Rapidity:
Computers can perform both professional and clerical tasks very quickly. The work which used to take hours to do can be done in a few minutes with the help of machines.
3. Accurate and Efficient Arrangement of Tasks:
This method can perform searching, storing, retrieving, distributing, accessing and abstracting in the catalog in an accurate and efficient manner than the manual method.
4. Sequential Arrangement:
Computers are able to perform various tasks with manually operated records. For example, it can be said that the computer can quickly arrange the selected data entries in order. Such as: Author, Title, Subject, Keywords, Call Number, Accession Number, ISBN Number etc. which is not possible with a hand-made catalog.
5. Accelerates Search Facilities:
Online systems can provide speed, search opportunities, modern / recent and comprehensive information which is not possible in OPAC, Biliofile, FabiP, Plus, CD-ROM, etc. which is not available manually.
6. Safe Time, Staff and Money:
Despite the high cost, if a system can be installed once to purchase and store computer components, it prevents wastage of time, people and money and can increase the value of the computer in the future.
7. Better Integration, Control and Efficiency:
Automated / online systems enable various libraries to integrate various internal functions between their branches and institute libraries. For example, it is able to connect for tasks such as ordering, classification, distribution, searching etc. As a result, the efficiency of time control work is proven.
8. Serves the Purpose of a Union Catalog
The Union Catalog serves as a central database for libraries, facilitating the management of resources across various branches. Its primary goal is to enhance the operations of the Central Library and its affiliated departmental or institute libraries. This method ensures that activities remain effective and organized by providing comprehensive access to library collections through a centralized system.
9. More up to date and higher productivity
The online system is more modern and efficient, boosting productivity significantly. In contrast, creating a catalog through traditional methods is a slow and time-consuming process, requiring several separate tasks, such as typing of shelf list , corporate author entry, Added entries, filling etc.
10. Improved standardization and collaborative facilities:
This system has the advantage of standard MARC format structure which allows for unprecedented real-time catalog sharing activities, exchange bibliographic records and other information at national and international levels through email and internet methods.
11. Enhances the image and status of librarians:
It is possible to enhance the image and professional status of librarians by using efficient and effective new technologies and by helping staff develop through continuous education of readers.
12. Encourages Creative and Innovative Urge:
The online system encourages creativity and innovation by overcoming the barriers and limitations of traditional indexing methods. It eliminates the monotony and lack of variety associated with manual work. Furthermore, it aims to transcend the constraints of provincial work, providing inspiration and confidence for new innovations.
Automatic/online cataloging systems have transformed library operations by ensuring faster processing, accurate organization, and wider accessibility of information.
Through standards like MARC and OPACs, libraries achieve better integration, resource sharing, and user-friendly search capabilities.
Overall, automated cataloging enhances productivity, professional efficiency, and the modern image of libraries and librarians alike.