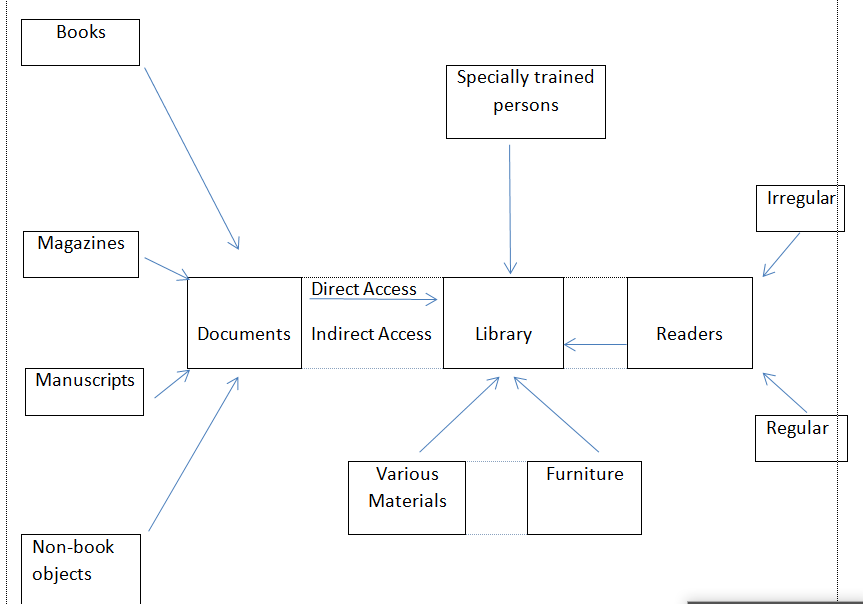
The conventional concept of a library is that it is an institution where manuscripts, books, periodicals, various types of non-book, non-printed documents are collected according to the needs and requirements of the readers, the collected documents are stored according to specific rules to be handed over to the customers in the shortest possible time according to their needs. To complete this entire activity, librarians use certain materials and follow specially trained methods. On the other hand, some materials are also provided to the customers, which help them find the required documents and information with minimum effort and time.
Therefore, it can be said that the library is a three-tier system where the interrelationships and working methods of these three levels collectively achieve a purpose. This can be shown through a table.
However, libraries are becoming accessible to users in new formats as times change. The library’s current use, presentation, and concept are more important than its size or collection. In the 1980s, CDS/ISIS books entered the era of edition. A notable introduction of this period was the Library of Congress’ MARC-1 and MARC-2 programs in 1968. However, with the advent of the Internet, a major change was seen in the library world. Starting in 1990, libraries started using the Internet in a slow manner, and by 1997-98, it was widely used in libraries. This Internet revolutionized library information collection and services. LAN, WAN, and Internet technologies helped to truly evaluate library science. At the same time, the invention, application, and use of library management software began.
In the first decade of the 21st century, libraries began to move in a new direction. With the help of library management software, the automation of conventional books got a direction. Before long, this automation system began to be experimented with and applied at a slightly more advanced level, which came to be known as the digital library.
There is no established definition of a digital library as such. Many people lump it in with a virtual library or an electronic library. Although the three concepts are distinct and there are subtle differences between them,. However, to be very specific, a digital library is a type of library whose acquisition, collection, and storage are in digital format (as opposed to print or other formats) and are accessible through computers. Digital information and documents are stored locally, which is different from a virtual library but can be accessed from any remote location through a computer network. A digital library is a type of information collection, storage, indexing, search, security, preservation, and retrieval system that provides convenient access to a large amount of digital information to compatible institutions.
The term “digital library” was first used in print in a 1988 report by the CNRI (Corporation for National Research Initiative). The term was later popularized by the NSF/DARPA/NASA Digital Library Initiative in 1994. Many popular digital libraries predate the Web, such as Projector Perseus, Project Gutenberg, ibiblio, etc.
Some digital records are created digitally; they are called native digital, while some digital records are created from print or other media through various processes; they are called converted digital records. Educational libraries have been very active in building institutional repositories of their own publications, books, periodicals, references, and various types of records in native digital or converted digital form. Many such institutional repositories are generally accessible to anyone, with some degree of control. Such institutional, truly free, freely accessible repositories of information are sometimes considered equivalent to digital libraries.
In a digital library, not only is there free access, but at the same time, numerous users can read, copy, or download a document or many documents. This copy can also be collected and stored on their own computer or in some other way. The necessary information is not only in text form, like books, but also in the form of audio, images, videos, and multimedia. Various documents can reach the user’s computer in an instant, at any geographical distance, at any time.
Digital Library vs Virtual Library:
The whole world is gradually moving towards digital systems. Libraries are no exception. Digital library basically means the next generation of library services through the application of the Internet and wave technology. In fact, a digital library is the creation, collection, preservation, management, distribution, and provision of services for various digital information documents and entities. A digital library can often be compared with an electronic library or a virtual library. Although there are several fundamental differences between them. An electronic library is very different from a digital library. Usually, conventional libraries collect and manage electronic resources, and, if necessary, the department from which physical transactions of documents like books are done is called an electronic library. This library mainly collects: CDs, floppy disks, video cassettes or audio cassettes, video or audio tapes, etc. Just like a book database, this resource repository is maintained and serviced.
On the other hand, a virtual library is very similar to a digital library. However, there are many fundamental differences between them. Although a virtual library must have all its collections digital, it does not mean that the entire digital library must be virtual. The main characteristics of a true virtual library are:
a) Its content is virtual;
b) Its presence is virtual;
c) Its accessibility is widespread;
d) Its users are unregulated and unspecified;
e) Its emphasis is on interoperability;
f) All activities are software-based;
From here, a comparison can be made between digital libraries and virtual libraries.
| Digital library | Virtual library | |
| Content | Locally collected but created in digital format | In digital format but global collection |
| Access and Ownership | Document has specific ownership | Only allows accessibility. |
| Classification | Accessibility of local resources | Local use of global resources |
| Standard | Usually MARC, Dublin Core, etc. are used. | The Z 39.50 OAI-PMH standard is commonly used. |
| Extension | Usually multi-subject | General Domain Dependent |
In summary, digital libraries focus on preserving and managing their own digital collections, while virtual libraries prioritize seamless access to a wide range of external resources. Although distinct, these two types of libraries complement each other in the modern information landscape.




